Following the piloting process of Advanced Manufacturing Labs for H/VET through the Collaborative Learning Factory (hereafter CLF), the EXAM4.0 partners we have piloted 16 technologies embedded in Industry 4.0.
The following image shows the overall structure of the piloting process.
Labs for Advanced Manufacturing-CLF
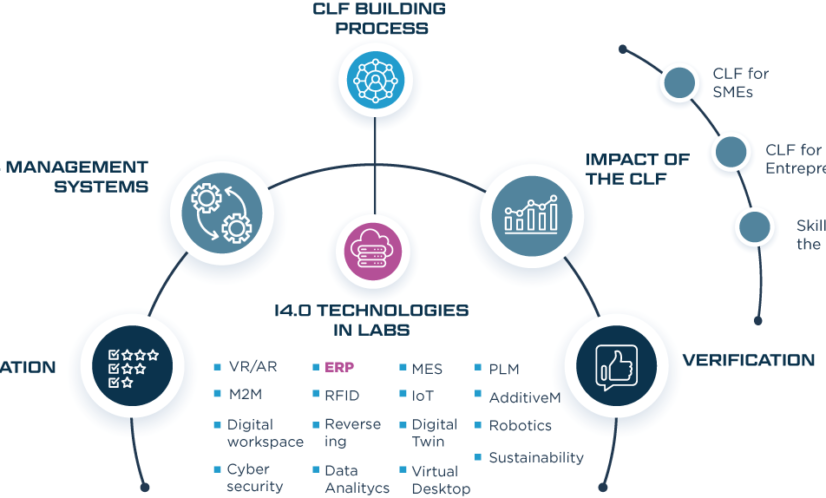
The present report is the one out of 16 I4.0 technology described within the “Industry 4.0 technologies in labs” section, specifically #14 Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP).
DEFINITION AND APPLICATION OF ERP IN INDUSTRY
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is the integrated management of main business processes, often in real time and mediated by software and technology. ERP is usually referred to as a category of business management software—typically a suite of integrated applications—that an organization can use to collect, store, manage, and interpret data from many business activities (Wikipedia, 2021).
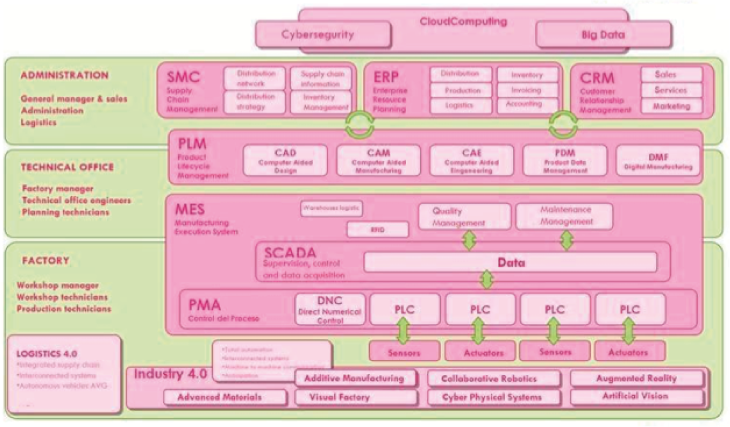
Figure 1: Integration of ERP-PLM-MES within the structure of the company. Source: Ibermatica
ERP automates more operational aspects of the business such as purchasing, sales, logistics, accounting, inventory and warehouse control, ordering, payroll, etc. The aim is to optimise business processes by connecting information linked to financial, production, cost or material demand management.
ERP is the set of processes that includes business and capacity planning, scheduling and customer order management. Accounting and Human Resources are part of these processes because they represent the management of all the resources (people, material, etc.) required to execute manufacturing.
The main functions of ERP that are relevant to manufacturing are the following:
- Capacity management —For every product to be manufactured, there is a defined process. There is also a maximum number of units that can be manufactured in a given time. This will affect both, the production order planning and the material procurement planning. The maximum capacity of a manufacturing plant is highly dependent on the number and mix of end products and how they are manufactured.
- Production planning — Adjusting the production plan according to changes in certain variables, including staff, is a major part of the production planning process. Planning must also account for changes in the current status of the production environment, as changes happen.
- Customer relationship management (CRM) — This function includes processes that ensure customer satisfaction with the end product. In addition, CRM anticipates the customer’s future demand and then recommends changes to the product line, accordingly with any details that would affect the manufacturing process.
- Supply chain management (SCM) — These processes ensure all materials, including raw materials and component parts, are delivered to the plant on time and adhere to the expected quality standards.
DIGITAL WORKPLACE IN HVET/VET LABS
In the case of Bidasoa, the integrated ERP system used is the software Odoo. It has an open source “community” version under the LGPLv3 license. It also has an enterprise version under commercial license that complements the community edition with commercial features and services, developed by the Belgian company Odoo S.A. (Odoo, 2021). At the moment, the ERP is used in the Mechanics department as a management tool and as an educational tool for the learning process of the students.
- Department management: with the aim of centralizing all actions in the management of the department.
- Occupation of spaces: the teaching staff can see the occupation of the different spaces used by the department in real time. In addition, as far as the Mechanics workshop is concerned, it is not only possible to know which group is there, but also who is at each machine.
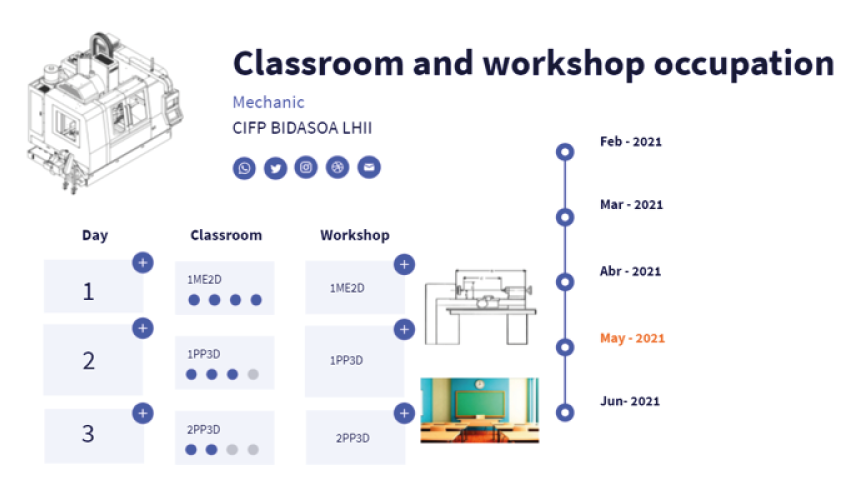
Figure 2: Bidasoa LHII ERP. Source: BidasoaLHII
- Stock management and purchasing: the control of both the stock of tools and the stock of raw material is done with this system. The situation in real time is known. Once the minimum number of materials is reached, the person in charge will contact the distributor to buy what is needed.
- Maintenance: the control of both class and lab is done. All breakdowns, needs,… that occur in computers, tablets, screens, software, machines,… are managed through failure reports which reach the person in charge. In this way, all the maintenance process is controlled from the moment the action is requested until it is done; who has done it, when it has been done and how much time and money it has cost. All maintenance reports are done with students, if possible, putting into practice corrective and preventive maintenance.
- Data exploitation: all the data obtained is used in the management of the department. Through the analysis of data, the improvement of processes, the optimisation of resources, decrease in breakdowns…. is obtained.
The CLF that is going to be launched has divided its production process into 4 stages (product design, process engineering, production and assembly) as can be seen in the following image. Within these stages, and taking into account the ERP-PLM-MES systems, the ERP is going to work in process engineering, production manufacturing and assembly stages.
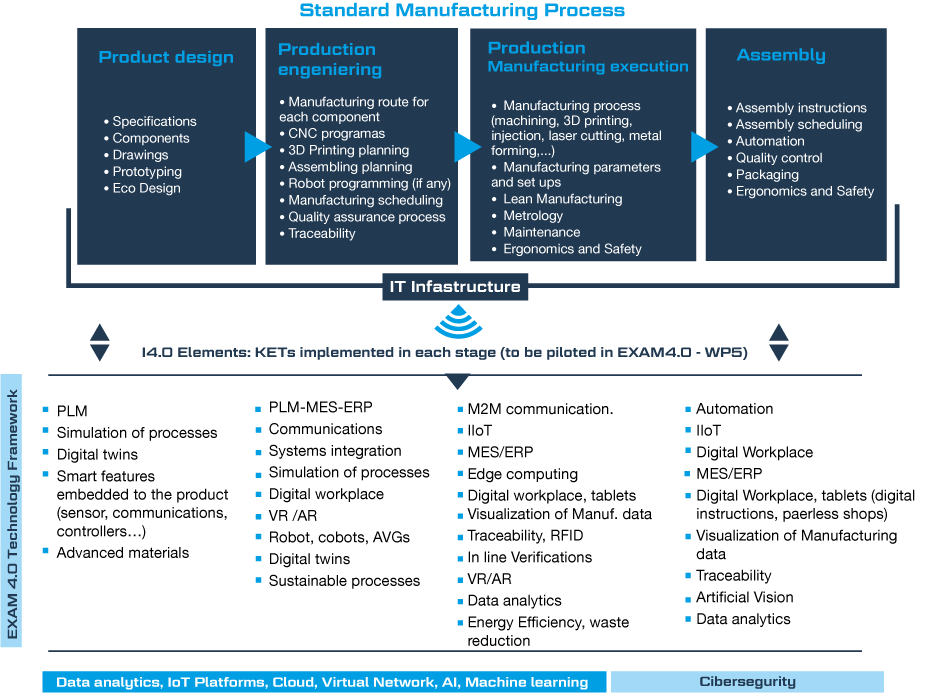
Figure 3: EXAM4.0 CLF value chain Source: Author’s creation
One of the objectives of the CLF is to be able to transfer data between labs, in order to control the manufacturing process. For this purpose, in the labs, there are going to be some technologies and machines that connected with sensors would transfer data through PLCs to a MES. This MES would be connected to the technical office part through a PLM and to the administrative part through an ERP. All this data would be transferred to the cloud to be later processed, always taking cybersecurity into account.
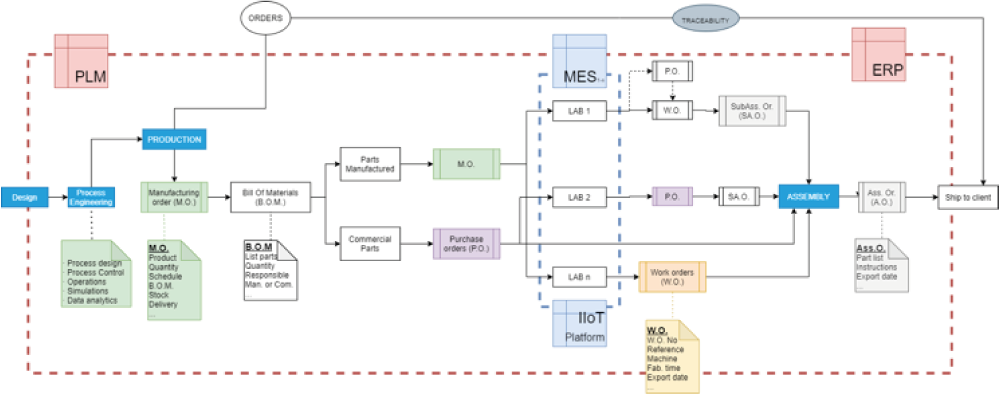
Figure 4: Possible diagram of the operation of the ERP-PLM-MES system of the CLF. Source: EXAM4.0
Taking into account all the production process, there must be a platform where orders can be placed. Here is where the ERP would start working. The order will have to reach a common ERP. This is important because it is from where the entire production process will be managed. In the first place, you will have to analyse if you have the necessary material in each lab for its manufacturing. In case there is not enough material in a lab, you will have to report it so that the corresponding purchase can be made. Secondly, taking into account the occupation of the machines in the different laboratories, you will have to send the manufacturing and assembly notice to the MES systems. At the same time, you will have to carry out the traceability to be able to follow the path and tell the customer when the product will be ready. Finally, it will take into account all the corrective and preventive maintenance of the labs; starting from the managing part, to customer data, stocks, etc.
The application of an ERP system in the CLF helps in the correct functioning of the process. Among other points it improves:
- Comprehensive management: manages and connects the desired areas (finance, purchasing, sales, warehouse, human resources and customer service, among others). In addition, this management system allows working with groups of companies, with multiple plants and different laws, currencies and languages.
- Predictability and quality: the data obtained from the ERP is converted into information for the improvement of the service, such as customer service, or improving the quality of the process, by anticipating breakages of stocks, machines, etc. It also provides necessary data for the correct application of continuous improvement.
- Control and flexibility: helps in the standardization of processes with fully customized workflows that help unify procedures.
The competencies acquired with the ERP can be classified into two groups: Technical and soft competences.
The technical competences are the ones that are most closely related to the technical content to be acquired in the learning process of the students, in this case Machining Technicians, Production Programming Staff and Industrial Design. Among other technical competences the main ones are:
- Greater awareness of the production process, from raw materials to part verification
- Calculation of costs and time
- Production scheduling
- Management of stocks (raw material, tools, etc.)
- Relationship with different suppliers
- Data analysis
- Improvements to be made in the production process
Secondly, as for the soft competences developed with ERP are:
Teamwork: being a collaborative tool, team members can plan their tasks and all have access to production sheets, control sheets….
Digital awareness: they get used to virtual working environments, understanding the data obtained, managing it and drawing conclusions.
Personal: autonomy, initiative, critical spirit, to be aware of the importance of good planning and to see how the decisions taken in the process affect them.
Communication: between different students, the one who plans the production with the one who executes it, being aware of the importance of the different explanations (verbal and written) that are given within the production process and that can help achieve a better result.
COLLABORATION OPPORTUNITIES OPENED BY ERP
The technology itself is a collaborative facilitator. It is the common system that unifies the different labs and distributes the jobs. From the information it collects, it enables different production processes of different schools or countries to be known. In addition, through collaboration, these processes could be improved or new ones could be created.
On the other hand, schools that do not have as much machinery or technology could make use of the data obtained, to be able to make practical cases of the different production processes.
The flexibility of the system makes it easy for other schools and other productive processes to become part of it.
